Gum Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by bacterial infection and inflammation of the gum tissues. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to serious oral health issues and tooth loss.
Addressing any signs of gum disease early can help prevent its progression and protect your oral health.
Dr.Bharadwaj Gupta
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (calculus), which cannot be eliminated by brushing alone. Tartar buildup irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and infection.
Other factors that can contribute to gum disease include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene
- Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Hormonal Changes
- Genetic Predisposition
- Previous Medical issues
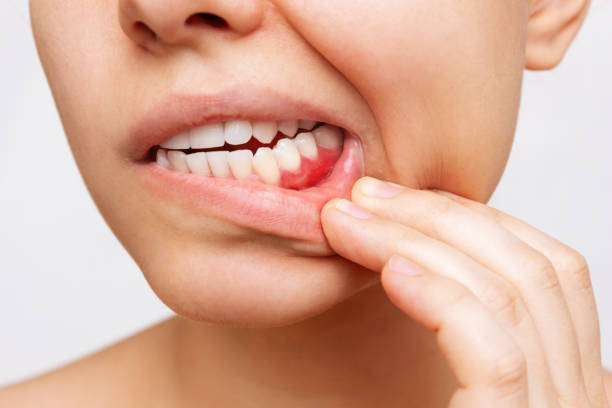
Symptoms of Gum Disease
The symptoms of gum disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums
- Bleeding Gums
- Bad Breath (Halitosis)
- Receding Gums
- Loose or Shifting Teeth
Treatment Options for Gum Disease:
The treatment for gum disease depends on its severity. Early stages of gum disease (gingivitis) can often be reversed with proper dental hygiene practices and professional cleanings.
However, if gum disease progresses to a more advanced stage (periodontitis), more intensive treatments may be required.
Prevention is key to avoiding gum disease. Practicing good oral hygiene, quitting smoking, and scheduling regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential to keeping your gums and teeth healthy.
If you notice any signs of gum disease, it is crucial to seek professional dental care promptly to prevent further complications and preserve your oral health.
Leave a reply